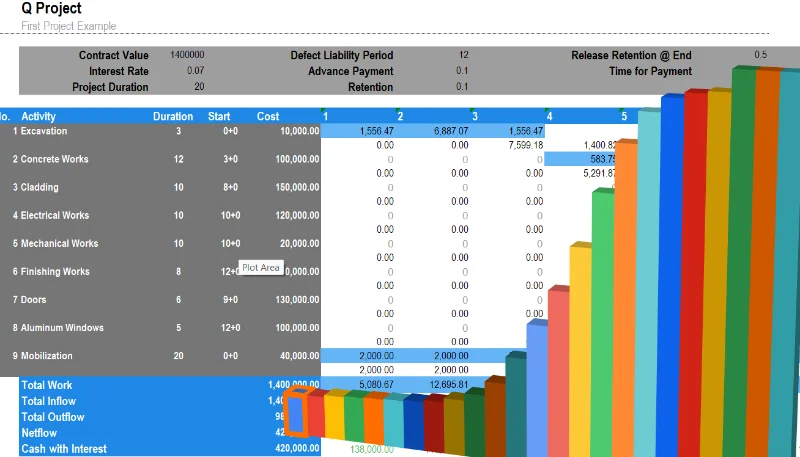
Advance Payment Major Risk in Construction Contracts
Introduction
Advance payments are a fundamental feature in many construction contracts, designed to facilitate the initiation and smooth progress of projects. These payments, typically made by the client to the contractor at the outset of a project, cover essential upfront costs such as mobilization, procurement of materials, and equipment setup. Despite their clear purpose, advance payments are sometimes misunderstood or misused, leading to disputes and inefficiencies. This article explores the purpose, contractual treatment, recovery mechanisms, and practical implications of advance payments in construction projects.
Purpose of Advance Payment
Advance payments serve as a critical financial tool to enable contractors to meet the demands of early-stage project requirements. Their primary purposes include:
-
Project Mobilization :Advance payments are most commonly allocated to mobilization activities, including site preparation, resource deployment, and initial material procurement. For example, the FIDIC Red Book (Clause 14.2) explicitly states that advance payments are intended to support these mobilization efforts.
-
Financial Support for Contractors :For contractors, particularly smaller firms, advance payments provide essential liquidity to manage initial expenses without resorting to external financing.
-
Risk Mitigation :By ensuring contractors have the necessary funds at the outset, advance payments reduce the likelihood of delays caused by financial constraints.
-
Addressing Common Misconceptions :A frequent misunderstanding is that advance payments serve to lock in material costs, thereby precluding contractors from claiming additional expenses due to price escalations. However, contracts like FIDIC and NEC make it clear that the primary role of advance payments is mobilization, not price stabilization.
Treatment of Advance Payments in Contracts
Different standard contracts address advance payments in distinct ways, reflecting their specific approaches to project management:
-
FIDIC Red Book :
- Advance payments are provided as an interest-free loan to contractors, primarily for mobilization.
- These payments are secured by Advance Payment Guarantees (APGs) and are typically recovered through deductions from interim payments.
-
NEC Contracts :
- Under Secondary Option X14 , advance payments are tied to early project activities, with recovery linked to milestones or progress.
-
JCT Contracts :
- Advance payments are treated as pre-payments for specified upfront costs and are strictly regulated in terms of use and recovery.
-
World Bank Standard Bidding Documents :
- Advance payments are phased and linked to guarantees to ensure accountability and minimize client risk.
-
Custom Contracts :
- Private contracts may link advance payments to specific deliverables or material procurement, though this is less common.
Recovery Mechanisms
The recovery of advance payments is a vital aspect of contract administration, ensuring transparency and fairness. Various contracts stipulate formulas for recovery, including:
-
Proportional Recovery Based on Progress (FIDIC) :
- Recovery is linked to the value of completed work:
-
Fixed Installments (JCT) :
- Payments are deducted in equal amounts over a specified number of interim payments:
-
Milestone-Based Recovery (NEC) :
- Recovery occurs upon the achievement of specific milestones:
-
Dynamic Recovery Linked to Progress (World Bank) :
-
Recovery adjusts with the percentage of work completed:
-
Recovery adjusts with the percentage of work completed:
Debate: Advance Payment as a Price Lock Mechanism
There is an allegation that advance payments are used to lock in material prices, preventing contractors from claiming additional costs due to price escalations. This claim warrants scrutiny:
-
Contracts Focus on Mobilization :Standard contracts like FIDIC and NEC explicitly define advance payments as funds for mobilization, not material price locking.
-
Short-Term Projects :Even in short-term projects, advance payments are typically insufficient to cover the total cost of materials required upfront. Additionally, logistical challenges make it impractical to procure and store all materials at the outset.
-
Long-Term Projects :For projects spanning over 18 months, material price fluctuations due to inflation, supply chain disruptions, and market dynamics render this approach entirely unfeasible. In such cases, price adjustment clauses are the appropriate mechanism for addressing cost escalations.
Opinion :The idea that advance payments should lock in material costs is fundamentally flawed, even for short-term projects. Contracts must clearly delineate the purpose of advance payments and include escalation clauses where long-term price volatility is a concern.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
-
Challenges :
- Mismanagement of funds by contractors, diverting them to other projects.
- Client liquidity constraints in releasing advance payments.
- Price escalations in the absence of adjustment clauses.
-
Mitigation Strategies :
- Advance Payment Guarantees (APGs) : Ensure recovery if the contractor defaults.
- Price Adjustment Clauses : Address material cost fluctuations effectively.
- Monitoring and Accountability : Regular audits and progress tracking to ensure proper utilization.
Conclusion
Advance payments are a crucial financial mechanism in construction projects, enabling contractors to mobilize resources and begin work efficiently. However, their purpose is often misunderstood. Advance payments are not intended to lock in material prices, even in short-term projects. For long-term projects, price adjustment clauses are essential to address cost escalation risks. To maximize the benefits of advance payments, clear contractual terms, effective recovery mechanisms, and diligent monitoring are imperative.
By understanding the purpose and limitations of advance payments, both clients and contractors can better navigate the complexities of construction projects, ensuring smoother execution and reduced financial risks.