Time Impact Analysis (TIA) – Construction Delay Method Explained
Introduction
Time Impact Analysis (TIA) is a highly effective method for evaluating the effects of delays on construction project timelines. It’s a prospective analysis method, predicting how new delay events might influence the future project completion date, and frequently required for Extension of Time (EOT) claims.
1. What Is Time Impact Analysis?
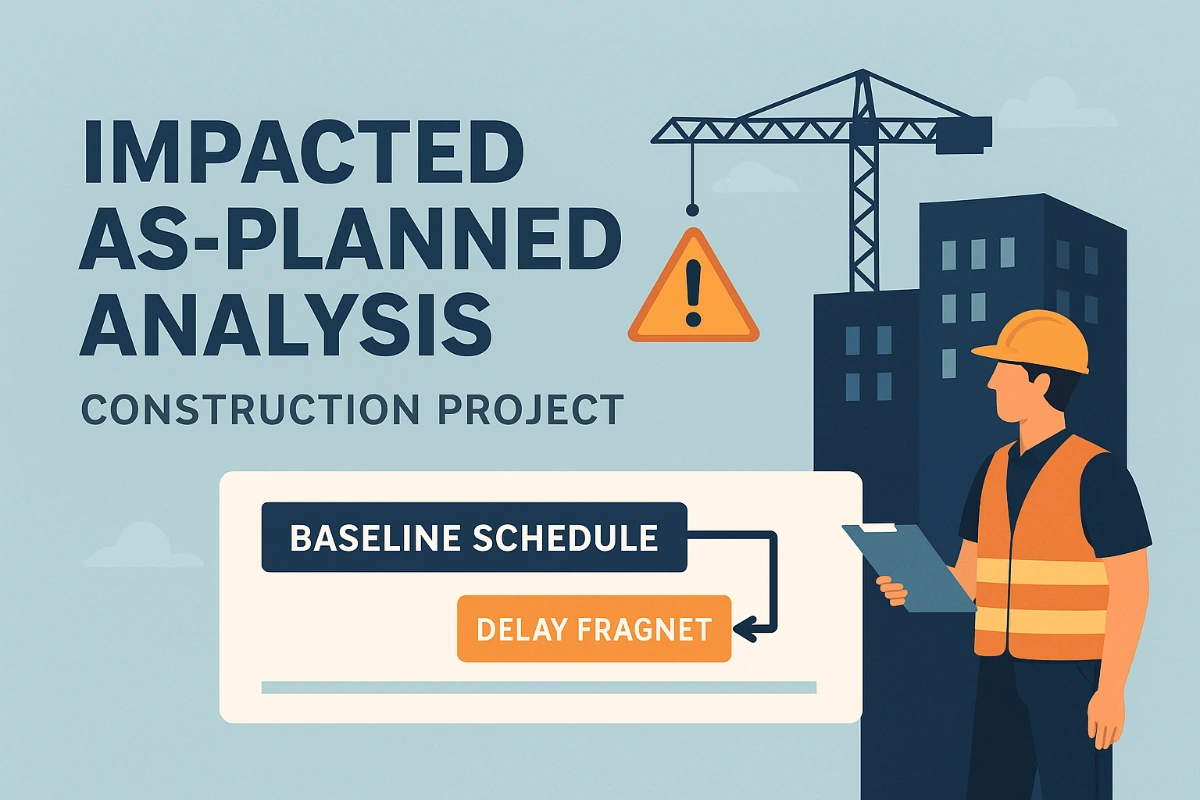
TIA involves inserting delay events directly into the current approved schedule to demonstrate their impact. Ideal for real-time delay assessment, it's widely recognized for its fairness and predictive capability.
2. How TIA Is Performed
Key steps include:
-
Baseline Selection: Use the latest approved schedule.
-
Insert Delay Fragment: Add a "fragnet" (activities representing the delay) at the date of occurrence.
-
Recalculate Schedule: Run a Critical Path Method (CPM) analysis to measure delay effects.
-
Document Impact: Clearly show the impact on critical path or new critical activities.
Example Application:
"If late procurement delays a critical activity by 10 days, inserting this delay into the schedule using a fragnet shows a corresponding 10-day extension to the project completion date." 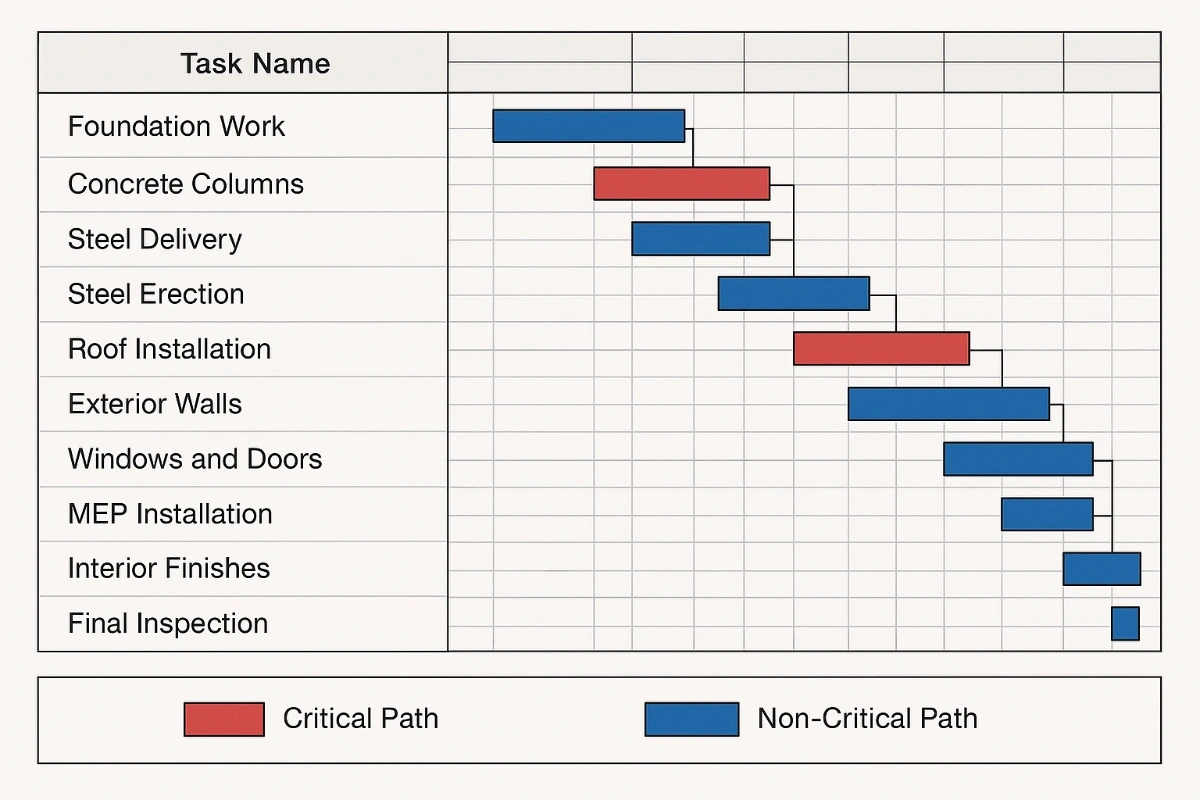
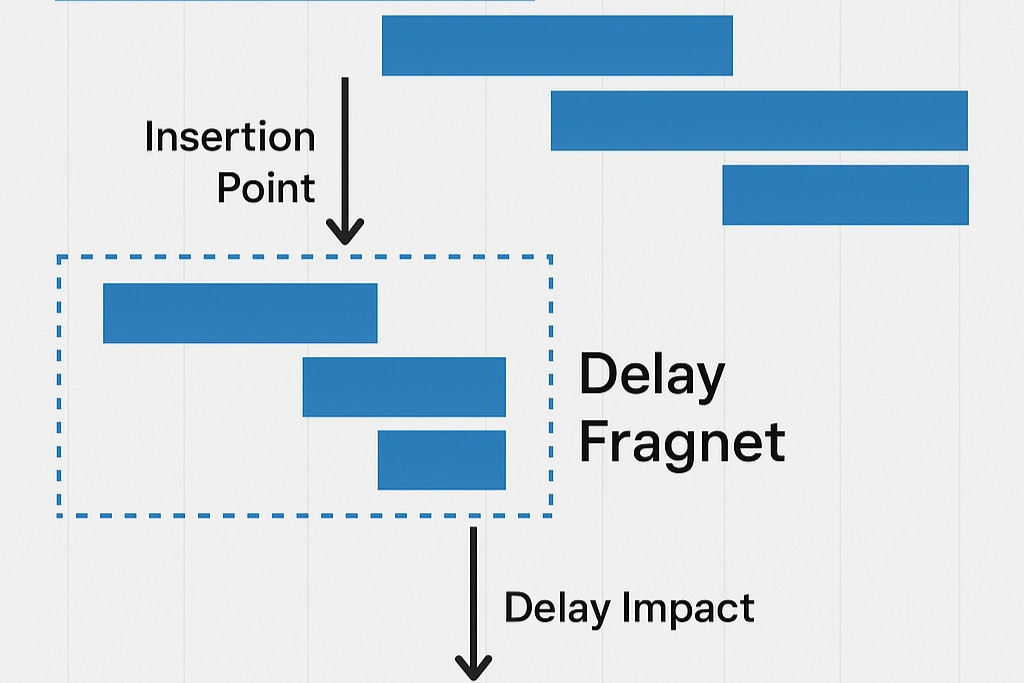
3. Key Contractual Considerations
Different contracts have varying TIA requirements:
-
FIDIC: Timely delay notices (Clause 20.2) and detailed substantiation required.
-
NEC: Emphasizes early warning and prospective analysis.
-
JCT: Clear documentation and immediate notification essential.
Common pitfalls:
-
Failure to notify delays promptly. Ready this about timely notices - Important!
-
Inadequate documentation or insufficient baseline updates.
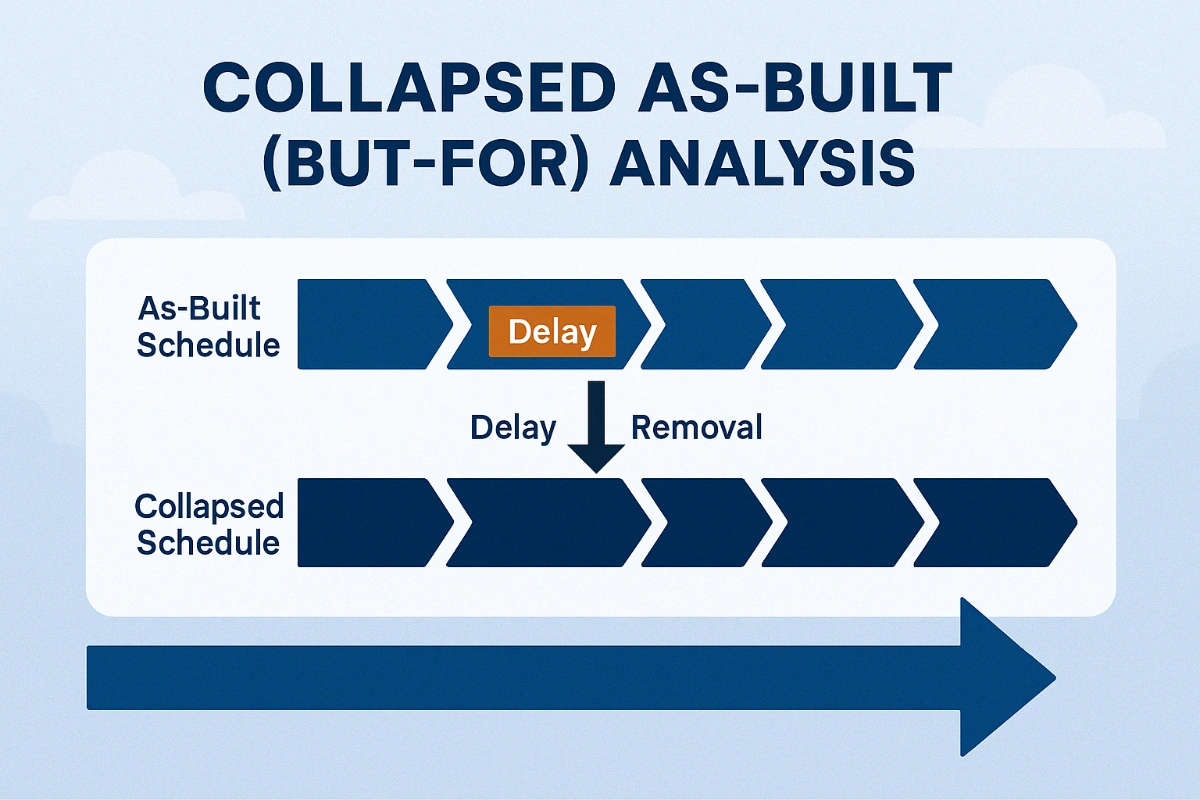
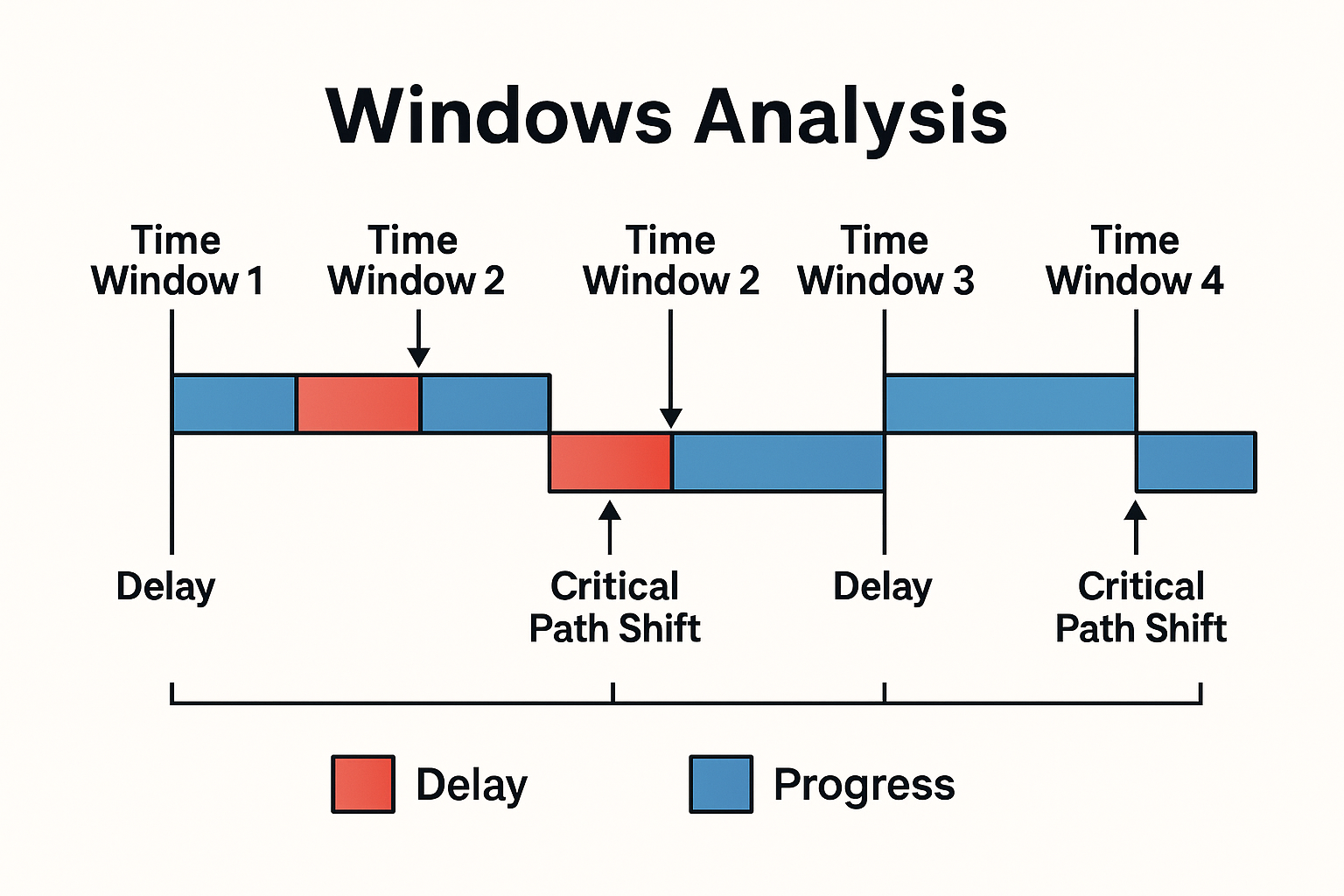
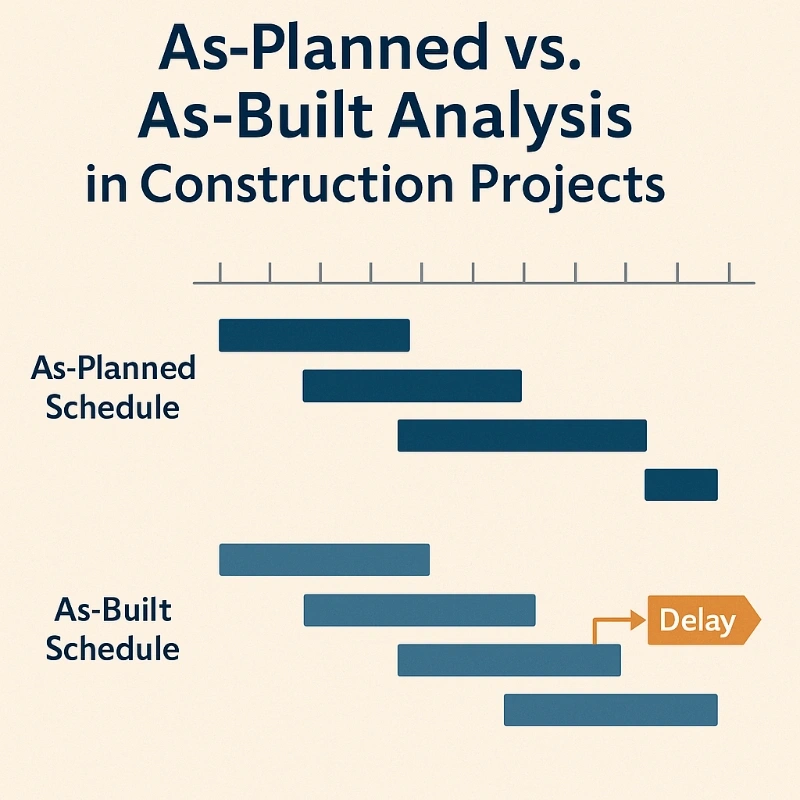
4. Comparison with Other Methods
| Method | Type | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| TIA | Prospective | Ongoing projects, real-time delays |
| As-Planned vs. As-Built | Retrospective | Completed projects, historical analysis |
| Window Analysis | Retrospective | Complex projects, phased delays |
Concurrent Delays: TIA clearly isolates impacts but should be paired with concurrency analysis when overlapping delays occur.
5. Best Practices for Effective TIA
-
Schedule Quality Checks: Maintain realistic and regularly updated baselines.
-
Fragnet Development: Ensure logical ties, accurate durations, and realistic sequencing.
-
Software Tips: Avoid common errors in Primavera P6/MS Project by regularly validating CPM logic.
6. Legal & Dispute Resolution Perspective
Courts and arbitrators widely accept TIA, scrutinizing it closely for signs of manipulation. Following recognized standards such as the SCL Delay & Disruption Protocol and AACEI RP 29R-03 enhances credibility.
7. Common Challenges & Mitigations
-
Disputed Baseline: Use contemporaneous and regularly updated schedules as supporting evidence.
-
Concurrent Delay: Integrate TIA with concurrency analysis to clearly delineate responsibilities.
8. Tools & Templates
Use these resources for stronger documentation and submissions:
Conclusion
Time Impact Analysis is essential for accurately assessing and documenting construction delays. Implementing best practices, understanding contractual requirements, and maintaining proper documentation ensures robust and defensible EOT claims.