Windows Analysis in Construction Delay Evaluation
Introduction
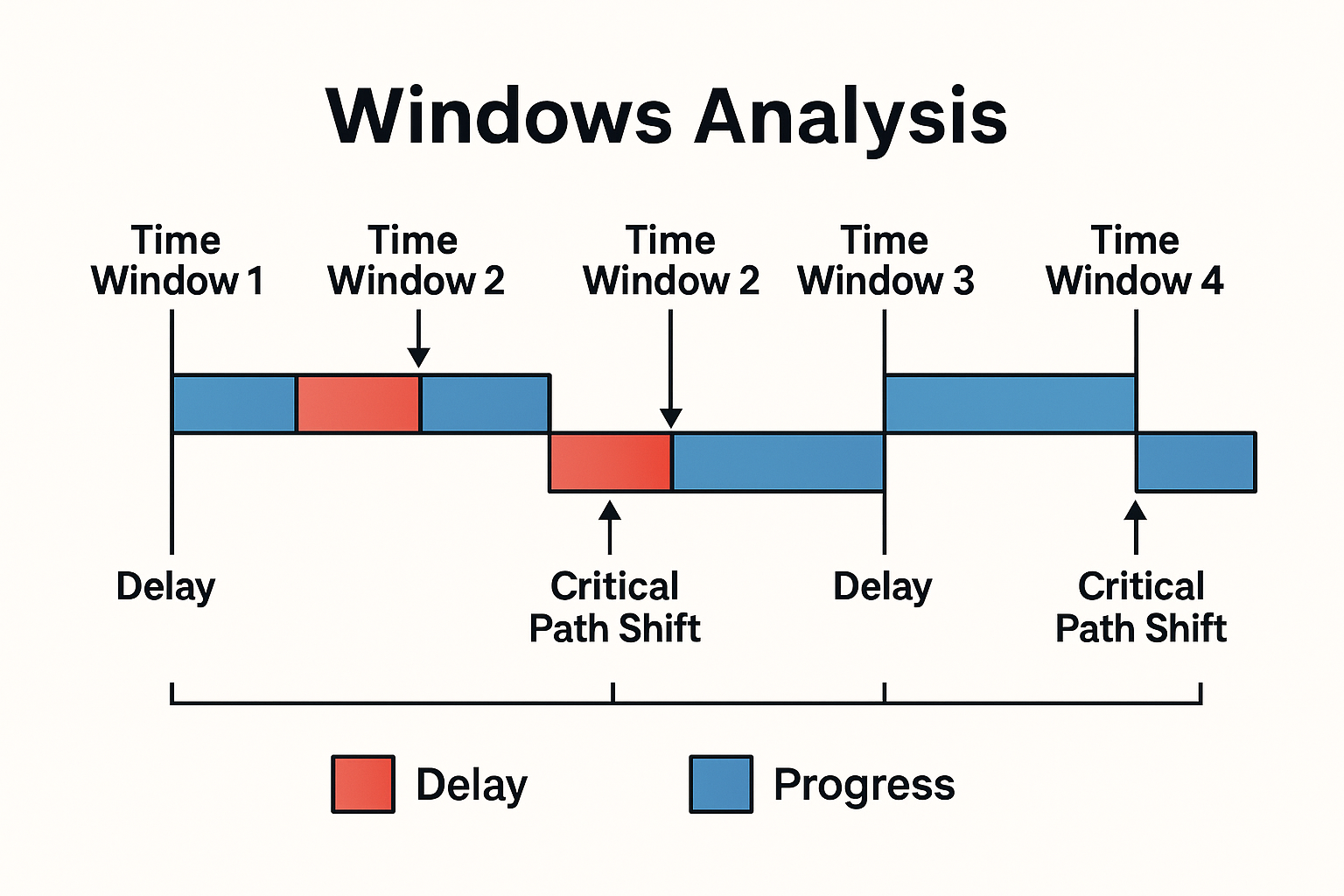
Windows Analysis is a widely recognized and robust delay analysis method that divides construction projects into specific periods or "windows" to systematically evaluate delays over time. It uniquely blends prospective (forward-looking) and retrospective (backward-looking) approaches—providing a dynamic and comprehensive view of delays, making it highly defensible in disputes.
1. What Is Windows Analysis?
Windows Analysis segments the project's timeline into discrete intervals ("windows") and compares planned schedules against actual progress within each window. By updating the schedule regularly, delays are evaluated progressively (prospectively), yet it also retrospectively reconstructs delay events after each window is completed.
-
Prospective component: Evaluates delays as they occur during each window, allowing proactive claim management.
-
Retrospective component: Uses actual as-built data from previous windows to reconstruct past delays accurately.
This hybrid approach makes Windows Analysis more credible in court or arbitration compared to static retrospective-only methods (e.g., As-Planned vs. As-Built).
2. How the Method Works
Step 1: Window Selection
Divide the schedule into intervals—either fixed intervals (e.g., monthly) or dynamic intervals (milestones or delay events).
-
Fixed intervals: Regular updates (monthly, quarterly), providing consistency.
-
Dynamic intervals: Tied directly to major milestones or significant delay events, offering precision.
Step 2: Analysis per Window
At each window’s closure, update the schedule with actual progress data. Perform delay assessment using critical path analysis within each window.
Step 3: Attribution
Clearly identify delays, their causes, and responsibilities, allocating responsibility window-by-window.
Step 4: Documentation & Integration
Continuously document findings and integrate data into delay logs, ensuring accuracy and transparency.
3. Real-World Case Example: Untangling Concurrent Delays
Consider a 12-month project split into quarterly windows. In Window 2:
-
Owner delay (late material delivery): 15 days
-
Contractor delay (labor shortage): 10 days, overlapping partially
Windows Analysis clarified that both delays overlapped by 5 days. Responsibility was proportionally allocated:
-
Owner: 15 days total
-
Contractor: 10 days total
-
Concurrent overlap: 5 days apportioned based on contractual terms
The result was a fair and transparent allocation accepted in arbitration proceedings.

4. Window Selection Criteria: Trade-offs
-
Smaller Windows (e.g., monthly):
-
Pros: High accuracy, easier identification of critical path shifts
-
Cons: Higher administrative effort, data-intensive
-
-
Larger Windows (e.g., quarterly, milestones):
-
Pros: Less administrative overhead
-
Cons: May obscure short-term critical path changes and delay events
-
Select window sizes based on project complexity, contract requirements, and available resources.
5. Common Pitfalls & Mitigation Strategies
-
Pitfall: Schedule Integrity ("Garbage In, Garbage Out")
-
Mitigation: Ensure baseline schedules are robust, validated, and regularly reviewed.
-
-
Pitfall: Critical Path Volatility (frequent shifts complicating attribution)
-
Mitigation: Integrate discrete delays using Time Impact Analysis (TIA) within windows. Cross-check findings with contemporaneous records like daily reports and delay logs.
-
6. Legal and Evidentiary Considerations
Courts and arbitration panels prefer Windows Analysis when:
-
Schedules are updated consistently (monthly, quarterly) in line with contract provisions.
-
Delay events are documented contemporaneously (daily reports, official delay notices, correspondences).
Case Law Example:
In Mirant vs. AECOM, Windows Analysis played a pivotal role in apportioning liability, demonstrating how well-maintained schedule updates and contemporaneous documentation strongly supported delay claims and defenses.
7. When to Use Windows Analysis
-
Complex or lengthy projects involving multiple delays and stakeholders
-
Projects requiring frequent schedule updates (FIDIC, NEC contracts)
-
Situations involving concurrent delays or multiple overlapping delays
8. Best Practices
-
Clearly define and consistently maintain window intervals.
-
Regularly update schedules and validate data integrity.
-
Pair windows analyses with comprehensive delay documentation (logs, notices, reports).
-
Cross-reference findings with methods like TIA for complex delays.
9. Get the Tools You Need for a Successful Windows Analysis
Make your delay evaluations more defensible with free, field-tested tools designed for real project conditions:
-
✅ Construction Delay Log Template – Track events across time windows with EOT references.
-
✅ Daily Site Delay Report Sample – Capture the day-to-day details that support your window-based analysis.
-
✅ EOT Claim Submission Checklist – Ensure each delay is backed by proper notices and documentation.
Conclusion
Windows Analysis provides unparalleled clarity in complex delay scenarios by systematically tracking and evaluating delays across distinct project phases. Its combined prospective and retrospective nature enhances credibility in formal claims and disputes. When supported by rigorous schedule management and contemporaneous records, Windows Analysis emerges as a highly effective and legally robust delay assessment method.