Inspection & Test Plan (ITP) in Construction — Complete Guide, Templates & Legal Essentials
Summary: An Inspection & Test Plan (ITP) tells the project team what must be inspected/tested, when, by whom, and against which acceptance criteria, with hold/witness points that control when work may proceed. A well-built ITP reduces rework, speeds approvals, and protects you contractually at handover.
1) What is an ITP?
An ITP (Inspection & Test Plan) is a structured plan of quality verifications across a activity, trade, or work lot. It sequences inspections and tests, references standards/specs, defines acceptance criteria, and sets Hold Points (stop until released) and Witness Points (notify; work may proceed if not attended). These controls are common across modern construction QA/QC systems.
Where it fits: ITPs sit under your Project Quality Plan / QMS and next to method statements, inspection checklists, and test reports.
2) Why ITPs matter (quality, cost, risk)
-
Defect prevention: Mandatory checks at critical stages prevent buried non-conformities that become costly later.
-
Traceability & evidence: Signed ITP records (checklists, tickets, lab reports, photos, calibrations) defend payment and certification.
-
Clarity for all parties: Clear responsibilities and notification windows reduce disputes and delays. (Also see ISO 9001’s emphasis on planned verification before release and documented evidence.)
3) Legal & contractual implications (FIDIC lens)
Under FIDIC forms, the Engineer has broad powers to inspect, test, reject, and instruct remedial work:
-
Inspection & Testing: FIDIC 1999 (Cl. 7—Plant, Materials & Workmanship) and 2017 updates enable the Engineer to require inspection/testing and to uncover work if notice wasn’t given. Costs of rework/re-testing due to non-compliance fall on the Contractor.
-
Delays around testing: If Employer/Engineer delays tests, the Contractor may be entitled to time and cost (e.g., FIDIC 1999 commentary on Cl. 7.4). fidic.org
-
Before Take-Over: Up to Taking-Over, the Engineer may instruct remedial work or removal and replacement of non-conforming Plant/Materials. Your ITP trail is your best defense.
Practical takeaway: Treat your ITP as a contract-compliance tool. Missing a Hold Point release or failing to notify can trigger uncovering at your cost and schedule risk.
4) Hold Points, Witness Points & Review/Surveillance
-
Hold Point (H): Mandatory verification gate—work shall not proceed until released by the authority (Engineer/Client/TPI).
-
Witness Point (W): Notify the authority; work may proceed if they don’t attend.
-
Review/Surveillance (R/S): Document review or spot checks.
These definitions are used consistently across industry platforms and government guidance.
5) Anatomy of an effective ITP (the columns you need)
Activity/Step • References (specs, drawings, codes) • Acceptance Criteria • Method/Procedure • Frequency/Sampling • Records/Evidence • Responsibility (C/S-C/E/TPI) • Point (H/W/R/S) • Notification window • Remarks.
Government QA frameworks (e.g., NSW) also emphasize identified records and planning documents inside the ITP/QMS.
6) How to write an ITP (step-by-step)
-
Start from scope/WBS → list the quality-critical operations.
-
Map standards & specs → define measurable acceptance criteria.
-
Insert control points → Hold/Witness at risk-heavy transitions (pre-cover, pre-pour, energization, pressure tests, etc.).
-
Define evidence → checklists, lab tests, batch tickets, photos, calibrations, as-built.
-
Assign responsibilities & notice → who signs, who attends, and how long before (e.g., 24–72h).
-
Link to NCR route → what happens if criteria aren’t met.
Industry templates echo this structure; see examples and downloadable shells below.
7) Trade-specific mini-ITPs (quick examples)
Concrete works: Pre-pour rebar (H), embedded items (W), truck tickets (S), slump/temperature (W/S), curing (S), stripping (W), compressive tests (S).
Structural steel: Material certs (S), fit-up (W), weld procedure/WPS & welder qual (H), visual/MPI/UT (W/S), coatings DFT (S).
MEP installs: Material approvals (S), pressure/leak tests (H/W), insulation (S), functional tests (W), start-up/commissioning (H for energization).
(These patterns are consistent with common ITP templates across construction and manufacturing.)
8) Roles & responsibilities
-
Contractor / Subcontractor: Prepare ITPs, notify, execute checks, keep records.
-
Engineer/Client Rep: Attend per Hold/Witness, release H-points, request uncovering, accept or reject.
-
Third-Party Inspector (TPI): As specified—often for statutory or specialized tests.
Clear attendance rights and notification lead-times are typical in public-sector QA specs.
9) Records, traceability & ISO 9001 alignment
Your ITP records are documented information in the QMS (ISO 9001:2015 Clause 7.5). Plan checks before release (Clause 8.6), control production under defined conditions (Clause 8.5.1), and control nonconforming outputs (Clause 8.7). Keep release evidence (who signed, criteria met) and NCRs with disposition and re-test results.
10) Non-conformance & re-testing
Missed criteria or failed tests → raise NCR, contain/correct, investigate root cause, re-inspect/test, and update the ITP pack. Under FIDIC, rework/re-testing due to Contractor non-compliance is generally at Contractor cost; ensure you can show planned arrangements and evidence.
11) Digital ITPs & execution tips
-
Use a digital ITP to push notifications for H/W points, capture e-signatures, and attach photos/lab reports for audit trails.
-
Keep lot-based ITP packs (link activity → records → NCRs).
(See modern platform guidance highlighting H/W/R use and mobile sign-offs.)
12) Free templates and examples (download & adapt)
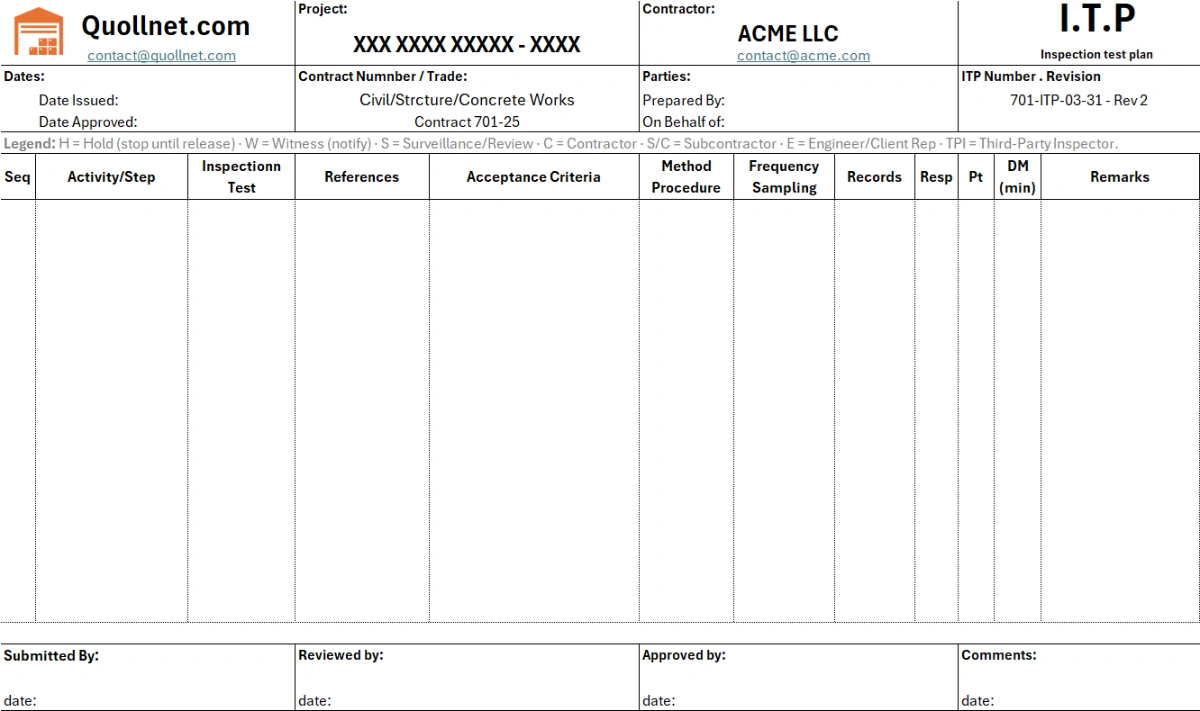
-
ITP | Inspection Test Plan (Excel): ready to customize inspection and test plan with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP form Excel template Excel Download
-
ITP | Inspection Test Plan (PDF): ready to customize inspection and test plan with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP form PDF template PDF Download - ITP | Inspection Test Plan (WebP): ready to customize inspection and test plan with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP form Image template WebP Download - Concrete ITP (Excel): ready to customize with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP example Excel template Excel Download
- Concrete ITP (PDF): ready to customize with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP example PDF template PDF Download
- Concrete ITP (WebP): ready to customize with H/W points, criteria, frequencies.
➜ITP example image template WebP Download










