Comprehensive Site Safety Checklist for Functionality of Tools and Equipment

Introduction:
Maintaining a safe work environment is paramount in any industry. A critical aspect of this is ensuring that all tools and equipment are in optimal working condition. Regular inspections not only prevent accidents but also enhance productivity by minimizing downtime. This comprehensive site safety checklist serves as a guide to assess the functionality of tools and equipment, ensuring that safety standards are consistently met.
Hand Tools Inspection
Power Tools Safety Measures
Heavy Equipment Evaluation
Ladders and Scaffolding Assessment
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Verification
Inspection and Maintenance Logs
Conclusion:
Regular inspections and maintenance of tools and equipment are foundational to workplace safety. By diligently following this comprehensive checklist, organizations can mitigate risks, ensure compliance with safety regulations, and promote a culture of safety. Remember, a proactive approach to equipment functionality not only safeguards employees but also enhances operational efficiency.
The Checklist:
Project: __________________ Date: ________________________ Time: _______________________
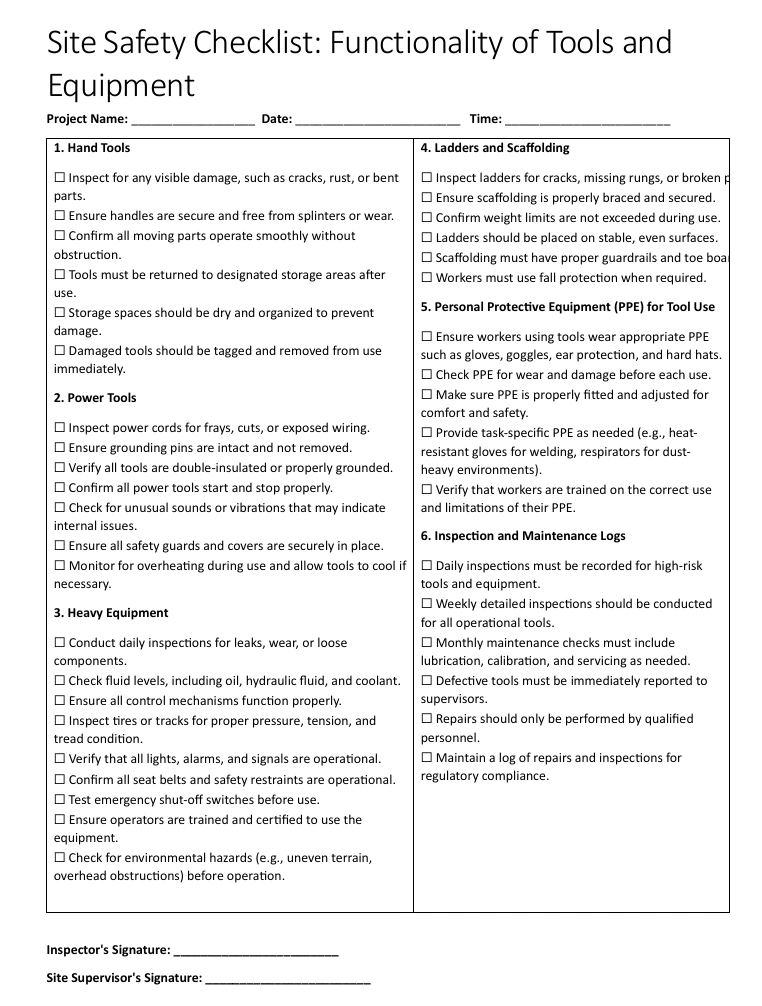
1. Hand Tools
- ☐ Inspect for any visible damage, such as cracks, rust, or bent parts.
- ☐ Ensure handles are secure and free from splinters or wear.
- ☐ Confirm all moving parts operate smoothly without obstruction.
- ☐ Tools must be returned to designated storage areas after use.
- ☐ Storage spaces should be dry and organized top revent damage.
- ☐ Damaged tools should be tagged and removed from use immediately.
2. Power Tools
- ☐ Inspect power cords for frays, cuts, or exposed wiring.
- ☐ Ensure grounding pins are intact and not removed.
- ☐ Verify all tools are double-insulated or properly grounded.
- ☐ Confirm all power tools start and stop properly.
- ☐ Check for unusual sounds or vibrations that may indicate internal issues.
- ☐ Ensure all safety guards and covers are securely in place.
- ☐ Monitor for overheating during use and allow tools to cool if necessary.
3. Heavy Equipment
- ☐ Conduct daily inspections for leaks, wear, or loose components.
- ☐ Check fluid levels, including oil, hydraulic fluid, and coolant.
- ☐ Ensure all control mechanisms function properly.
- ☐ Inspect tires or tracks for proper pressure, tension, and tread condition.
- ☐ Verify that all lights, alarms, and signals are operational.
- ☐ Confirm all seat belts and safety restraints are operational.
- ☐ Test emergency shut-off switches before use.
- ☐ Ensure operators are trained and certified to use the equipment.
- ☐ Check for environmental hazards (e.g., uneven terrain, overhead obstructions) before operation.
4. Ladders and Scaffolding
- ☐ Inspect ladders for cracks, missing rungs, or broken parts.
- ☐ Ensure scaffolding is properly braced and secured.
- ☐ Confirm weight limits are not exceeded during use.
- ☐ Ladders should be placed on stable, even surfaces.
- ☐ Scaffolding must have proper guardrails and toe boards.
- ☐ Workers must use fall protection when required.
5. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for Tool Use
- ☐ Ensure workers using tool swear appropriate PPE such as gloves, goggles, ear protection, and hard hats.
- ☐ Check PPE for wear and damage before each use.
- ☐ Make sure PPE is properly fitted and adjusted for comfort and safety.
- ☐ Provide task-specific PPE as needed (e.g., heat-resistant gloves for welding, respirators for dust-heavy environments).
- ☐ Verify that workers are trained on the correct use and limitations of their PPE.
6. Inspection and Maintenance Logs
- ☐ Daily inspections must be recorded for high-risk tools and equipment.
- ☐ Weekly detailed inspections should be conducted for all operational tools.
- ☐ Monthly maintenance checks must include lubrication, calibration, and servicing as needed.
- ☐ Defective tools must be immediately reported to supervisors.
- ☐ Repairs should only be performed by qualified personnel.
- ☐ Maintain a log of repairs and inspections for regulatory compliance.
Inspector's Signature: ________________________
Site Supervisor's Signature: ________________________

Download Section:
To facilitate the implementation of this checklist, we offer downloadable resources in various formats:
Download free safety check list for functionality of tools and equipment in word format
Download free safety check list for functionality of tools and equipment in Excel format
Download free safety check list for functionality of tools and equipment in pdf format
Download free safety check list for functionality of tools and equipment in image format
Reference Section:
For further reading and authoritative guidelines, consider the following resources:
- OSHA Hand and Power Tools Inspection Checklist
- Construction Safety Inspection Checklist by Texas Department of Insurance
- Workshop and Tool Safety Checklist by Safesite












