Material Requisition Sheet (MRS): Definition, Purpose, Risks, and Best Practices
In every construction or engineering project, the flow of materials determines whether the project runs smoothly or stalls in costly delays. Among the essential documents that ensure materials arrive where and when needed is the Material Requisition Sheet (MRS).
This article offers a complete guide to the MRS — covering its purpose, workflow, key components, codification, relation to the project budget and BOQ, its role in stock management, common risks, and best practices. Unlike many brief explanations online, this article provides a comprehensive, industry-level reference. It also includes free downloadable MRS templates in Word, Excel, and PDF formats for immediate use.
📥 Download Templates:
What is a Material Requisition Sheet?
A Material Requisition Sheet (MRS) is an internal document used to formally request materials required for a project. It originates from the site team (engineer, supervisor, or foreman) and flows through an approval cycle before procurement, stores, or warehouse teams release the material.
It is not a purchase order; rather, it is the step before a purchase order, acting as the internal authorization for materials to be acquired or issued.
Different Names for MRS
Organizations may call the MRS by different names, including:
-
Material Requisition (MR)
-
Material Request Form (MRF)
-
Material Requisition Note (MRN)
-
Store Requisition Slip
-
Internal Requisition Form
-
Materials Demand Sheet
Regardless of the label, the purpose remains consistent: to control and document material requests.
Purpose of a Material Requisition Sheet
-
Timely Procurement: Ensures materials are requested and delivered before they are needed on site.
-
Cost Control: Prevents unauthorized or excessive material consumption.
-
Accountability: Documents who requested the material, who approved it, and why.
-
Coordination: Bridges site engineers, procurement teams, and stock managers.
-
Audit Trail: Creates a paper or digital record of project material movement.
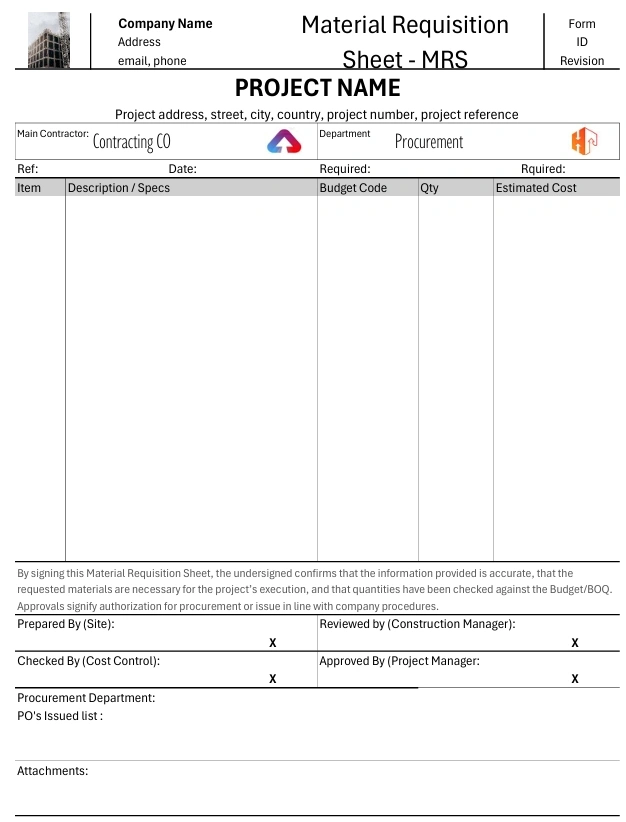
Key Components of a Material Requisition Sheet
A standard MRS typically includes:
-
Project and department details
-
Material description (name, grade, specification)
-
Quantity and unit of measurement
-
Required delivery date
-
Requester details (engineer/site manager)
-
Approver details (project/procurement manager)
-
Remarks or special instructions
-
Material Code (see codification section)
Workflow of a Material Requisition
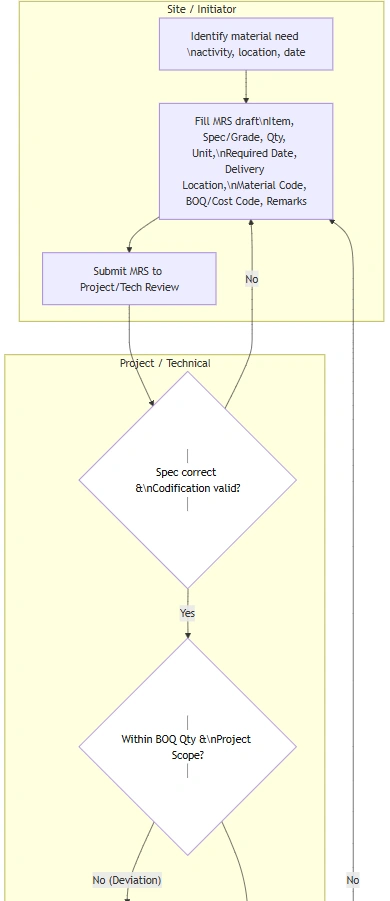
-
Need Identification – Site engineer identifies required material.
-
Requisition Submission – MRS is filled and sent for review.
-
Verification – Project manager checks BOQ, budget, and stock.
-
Approval – Approver signs and forwards to procurement.
-
Procurement / Store Action – Either purchase order is raised or material is released from existing stock.
-
Delivery & Record – Material delivered to site, logged by stock manager, and recorded against requisition.
MRS Full Workflow in SVG format (can be opened in browser)
Relation with Project Budget and BOQ
The Bill of Quantities (BOQ) serves as the benchmark for planned material quantities. The MRS ensures that:
-
Material requests align with BOQ allowances.
-
Any deviation or excess consumption is flagged.
-
Procurement is linked directly to project budget allocations.
-
Management can monitor variance between planned and actual material usage, helping detect overruns, design changes, or inefficiencies.
Without this control, projects risk overspending and disputes with clients over unbudgeted claims.
Relation with Project Stock and Stock Manager
The MRS directly interacts with both project stock and organization-wide stock:
-
The site storekeeper/stock manager checks if materials are available before forwarding the request to procurement.
-
The organization warehouse may supply bulk items already purchased, reducing cost and procurement lead time.
-
Accurate records ensure accountability for which materials were consumed, by which department, and for what activity.
-
Integration with digital stock systems prevents duplicate or unnecessary orders.
This link between requisition and stock control is what makes the MRS a cornerstone of efficient inventory management.
Codification in Material Requisition Sheets
One of the most overlooked but powerful aspects of MRS is codification.
Why Codification Matters:
-
Accuracy: Prevents confusion between similar materials (e.g., 10mm vs. 12mm rebar).
-
Consistency: Uniform identification across projects and departments.
-
Integration: Directly links with ERP, inventory, and cost control systems.
-
Control: Prevents duplicate purchases and ensures traceability.
Example Codification Scheme:
-
Cement (OPC 50kg bag) → CEM-001
-
Steel Rebar 12mm → STL-012
-
Electrical Cable 16mm² → ELE-016
Every employee filling an MRS must be trained to use company codification standards. This ensures that requisitioned items can be instantly validated and tracked in both project and organizational stock systems.
Risks of Poorly Managed Material Requisitions
-
Project Delays: Late approvals or missing requisitions can halt construction.
-
Overstocking: Excess ordering leads to storage costs and risk of deterioration.
-
Budget Overruns: Requisitions not tied to BOQ inflate project costs.
-
Material Wastage: Wrong specifications ordered due to poor codification.
-
Fraud or Misuse: Uncontrolled requisitions may result in theft or diversion.
-
Audit Issues: Lack of documentation weakens financial and compliance audits.
Benefits and Best Practices
-
Efficiency: Smooth flow of materials without site delays.
-
Transparency: Clear documentation of who requested and approved.
-
Budgetary Discipline: Requests matched to BOQ and project cost plan.
-
Best Practices:
-
Use standardized formats across projects.
-
Enforce codification for every material.
-
Define approval hierarchies clearly.
-
Adopt digital requisition systems with auto-validation.
-
Digital Transformation of MRS
Modern projects are moving away from paper-based requisitions to digital MRS platforms:
-
Real-time tracking: Users can check status instantly.
-
Stock validation: System checks existing stock before approving.
-
Budget linkage: Requests cross-checked against BOQ and cost codes.
-
Audit trails: Timestamps, versioning, and approval logs.
-
Templates: Digital systems often provide auto-filled requisition templates.
Digital transformation not only improves efficiency but also reduces fraud, errors, and delays.
Example Scenario: How MRS Works in Practice
A site engineer on a high-rise project identifies that 200 bags of OPC Cement are needed for slab casting.
-
Engineer fills MRS:
-
Item: OPC Cement 50kg bag
-
Code: CEM-001
-
Quantity: 200 bags
-
Required by: 15th June
-
-
Project manager checks:
-
BOQ shows cement allocation is sufficient.
-
Project store has only 40 bags left.
-
-
Approval: Project manager approves and forwards to procurement.
-
Procurement action: Since stock is insufficient, procurement raises PO for 160 bags.
-
Delivery: Warehouse delivers, stock manager updates balance.
This single cycle ensures accountability, budget control, and timely delivery.
Free Downloadable Templates
To help professionals implement MRS in their organizations, we provide ready-to-use templates:
📥 Download Now:
These templates can be customized to fit your company’s codification system and approval workflow.
Conclusion
The Material Requisition Sheet (MRS) is more than just a form; it is a control mechanism that connects site engineers, procurement teams, stock managers, and financial controllers. By linking directly to the BOQ, enforcing codification, and integrating with stock and digital systems, the MRS becomes a backbone of project material management.
Whether you are managing a small site or a multi-million-dollar project, adopting structured requisition processes — and making use of standardized templates — is essential for transparency, efficiency, and cost control.
📥 Don’t forget to download your free MRS templates in Word, Excel, and PDF to start implementing best practices today.