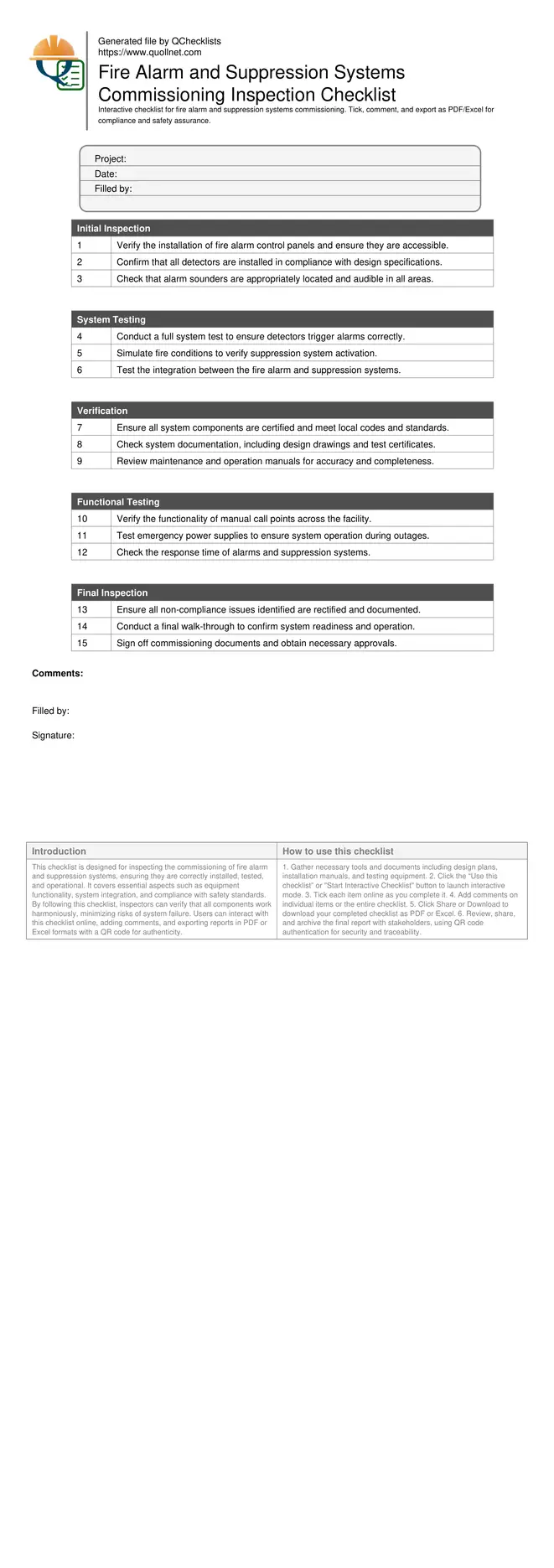
Fire Alarm and Suppression Systems Commissioning Inspection
This checklist is designed for inspecting the commissioning of fire alarm and suppression systems, ensuring they are correctly installed, tested, and operational. It covers essential aspects such as equipment functionality, system integration, and compliance with safety standards. By following this checklist, inspectors can verify that all components work harmoniously, minimizing risks of system failure. Users can interact with this checklist online, adding comments, and exporting reports in PDF or Excel formats with a QR code for authenticity.
- Ensure fire alarm systems are correctly installed and operational, reducing risks of malfunction.
- Verify suppression systems meet safety standards, providing peace of mind for occupants.
- Check system integration for seamless operation during emergencies.
- Interactive online checklist with tick, comment, and export features secured by QR code.
Initial Inspection
System Testing
Verification
Functional Testing
Final Inspection
Importance of Commissioning Inspections
Commissioning inspections ensure that fire alarm and suppression systems are not only installed correctly but are also fully operational and integrated. These checks are crucial to ensure that the system will function as intended in the event of a fire, providing maximum safety for building occupants. Regular and thorough inspections can also help in identifying potential malfunctions before they occur.
- Prevents system failures during emergencies.
- Ensures compliance with safety standards.
- Increases confidence in system reliability.
Common Issues in Fire System Installations
Even with the best planning, issues can arise during the installation of fire systems. Common problems include incorrectly positioned detectors, inadequate alarm audibility, and improper system integration. Addressing these issues during commissioning can prevent costly repairs and ensure the system functions as designed.
- Incorrect detector placement affects performance.
- Poor alarm audibility can lead to safety risks.
- Integration issues may prevent full system activation.
How to Use This Checklist for Fire Alarm and Suppression Inspection
- Gather necessary tools and documents including design plans, installation manuals, and testing equipment.
- Click the “Use this checklist” or "Start Interactive Checklist" button to launch interactive mode.
- Tick each item online as you complete it.
- Add comments on individual items or the entire checklist.
- Click Share or Download to download your completed checklist as PDF or Excel.
- Review, share, and archive the final report with stakeholders, using QR code authentication for security and traceability.
Call to Action
- Start Checklist Tick off tasks, leave comments on items or the whole form, and export your completed report to PDF or Excel—with a built-in QR code for authenticity.
- Download Excel - Fire Alarm and Suppression Systems Commissioning Inspection
- Download PDF - Fire Alarm and Suppression Systems Commissioning Inspection
- View Image - Fire Alarm and Suppression Systems Commissioning Inspection
Cite & Embed
“Fire Alarm and Suppression Systems Commissioning Inspection by Quollnet”
with a link to
this source page.