Temporary Fencing and Site Access Inspection Checklist
Definition: Temporary Fencing and Site Access Inspection validates perimeter fencing, gates, signage, and emergency egress for active worksites, ensuring compliance with plans and authority requirements for safe, controlled access.
- Verify fence height, stability, and gaps with measurements and photos.
- Confirm gates, latches, and sightlines enable safe, controlled movements.
- Check signage visibility, languages, and night illumination for clear guidance.
- Interactive, commentable checklist with export and QR code verification.
Temporary Fencing and Site Access Inspection ensures that temporary perimeter barriers, entry gates, safety signage, and emergency routes align with approved plans and keep people and assets safe. This focused scope covers temporary site fencing inspection, site access control, and perimeter security checks around construction and maintenance works. By confirming fence height, stability, and anti-climb features, you deter trespass and reduce collapse risks. By validating gate width, closers, and locking, you prevent vehicle–pedestrian conflicts. By auditing signage and wayfinding, you guide deliveries, visitors, and responders reliably, day and night. And by proving emergency egress routes are clear, lit, and measured, you avoid blocked exits, fines, and shutdowns. Use this interactive checklist to capture readings, photos, and stakeholder sign-offs in one place. Tick items on mobile, add comments for issues, assign actions with due dates, and export as PDF/Excel—each record secured by a unique QR.
- Establishes a defensible perimeter with measurable criteria—height, gaps, ballast, and connections—so barriers resist climbing, wind, and tampering. Evidence includes photos with scales, torque values for clamps, and geotagged positions. This method reduces collapse, encroachment, and unauthorized entry while aligning with approved drawings and authority requirements.
- Protects people and plant at gates by verifying widths, swing direction, closers, latches, and sightlines. Clear queuing space, level thresholds, and visible stop points support safe movements. Logs, permits, and lock numbers create traceability. Illumination and reflective signs maintain visibility during dawn, dusk, and night operations.
- Interactive online checklist with tick, comment, and export features secured by QR code. This enables field teams, supervisors, and clients to collaborate in real time, attach photos, tag nonconformances, and close actions. Exports provide audit-ready records for toolbox talks, progress meetings, and regulatory inspections.
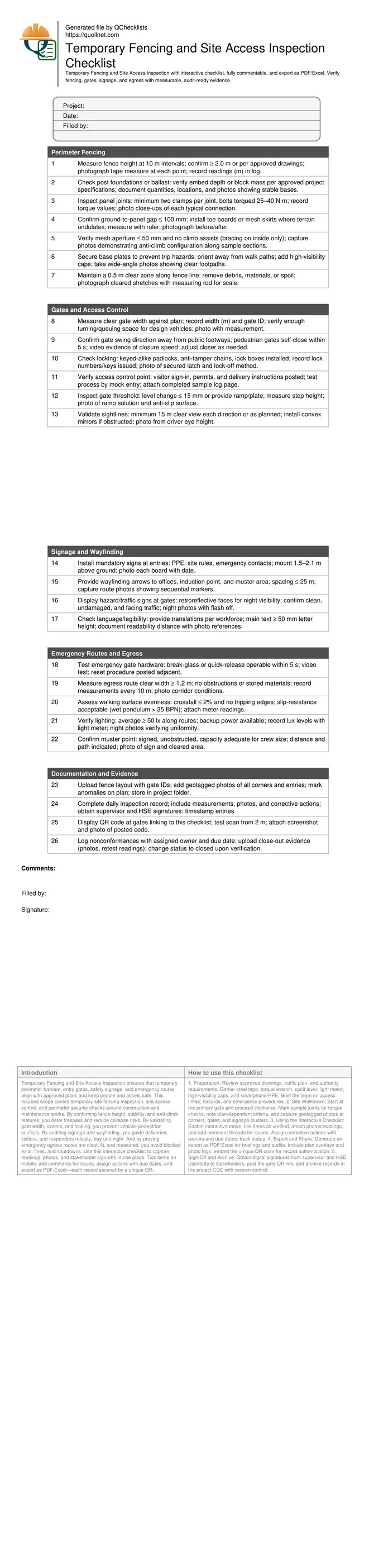
Perimeter Fencing
Gates and Access Control
Signage and Wayfinding
Emergency Routes and Egress
Documentation and Evidence
Scope and Safety Outcomes
This checklist focuses on temporary perimeter protection and controlled access for active worksites. It limits scope to fencing systems, gates, signage, and emergency egress routes, avoiding permanent works or unrelated traffic management plans. By measuring fence heights, securing joints, and minimizing ground gaps, you reduce climbability and wind-related failures. Gate checks verify widths, swing direction, closers, and locking—controlling who enters and how vehicles interface with pedestrians. Signage and wayfinding steps confirm visibility and understanding, including at night and for multilingual crews. Egress measures ensure routes remain clear, lit, and quickly operable in an incident. Each item captures objective evidence—photos, readings, IDs, and signatures—creating audit-ready records. The result is a safer perimeter, fewer stoppages, and traceable compliance per approved project specifications and authority requirements.
- Single-subject scope: fencing, gates, signage, egress.
- Objective evidence: photos, measurements, signatures.
- Measurable cues reduce ambiguity and disputes.
- Night visibility and multilingual clarity addressed.
- Aligns with approved plans and authority requirements.
Field Methods and Acceptance Cues
Inspectors should carry a steel tape, torque wrench, light meter, spirit level, and smartphone for geo-tagged photos. Start by walking the full perimeter, marking panel joints to be sampled for torque checks. Measure fence height at set intervals, photographing the tape against the mesh. Assess base plates and ballast, confirming stability without creating trip hazards. At gates, time the self-closure and verify latch engagement. Measure threshold steps and sightlines from driver eye height. For signage, verify mounting heights, letter size, reflectivity, and nighttime legibility by light-meter readings. On emergency routes, confirm clear widths, evenness, slip resistance, illumination, and quick-release hardware function. Record every reading in SI units and link photos to plan locations. If a criterion is plan-dependent, reference the drawing number and sheet to avoid ambiguity.
- Carry calibrated tape, torque wrench, light meter.
- Photograph measurements against the asset surface.
- Reference drawing numbers for plan-dependent criteria.
- Time gate closures and release mechanisms.
- Record SI units consistently in logs.
Real-World Pitfalls and Quick Fixes
Common failures include panels lifted by uneven ground, gates that drag due to rutting, and signs hidden by parked plant. Quick fixes: add mesh skirts or toe boards to close ground gaps; re-level bases or add ballast for stability; fit ramps or plates at thresholds; move signage above vehicle sightlines; and install convex mirrors where obstructions persist. At night, inadequate lighting undermines otherwise sound setups—verify lux and add temporary floodlights as needed. Language barriers can dilute instructions; provide concise, pictogram-supported signage and translations matching workforce languages. For emergency gates, routinely test quick-release functions and keep reset instructions adjacent. Finally, close the loop by logging nonconformances with owners and due dates, then retest promptly.
- Close ground gaps with skirts or toe boards.
- Stabilize bases; re-level and add ballast.
- Raise, clean, and space signage for visibility.
- Install mirrors to improve sightlines.
- Test and document emergency releases routinely.
How to Use This Interactive Checklist
- Preparation: Review approved drawings, traffic plan, and authority requirements. Gather steel tape, torque wrench, spirit level, light meter, high-visibility caps, and smartphone/PPE. Brief the team on access times, hazards, and emergency procedures.
- Site Walkdown: Start at the primary gate and proceed clockwise. Mark sample joints for torque checks, note plan-dependent criteria, and capture geotagged photos at corners, gates, and signage clusters.
- Using the Interactive Checklist: Enable interactive mode, tick items as verified, attach photos/readings, and add comment threads for issues. Assign corrective actions with owners and due dates; track status.
- Export and Share: Generate an export as PDF/Excel for briefings and audits. Include plan overlays and photo logs; embed the unique QR code for record authentication.
- Sign-Off and Archive: Obtain digital signatures from supervisor and HSE. Distribute to stakeholders, post the gate QR link, and archive records in the project CDE with version control.
Call to Action
- Start Checklist Tick off tasks, leave comments on items or the whole form, and export your completed report to PDF or Excel—with a built-in QR code for authenticity.
- Download Excel - Temporary Fencing & Site Access Inspection
- Download PDF - Temporary Fencing & Site Access Inspection
- View Image - Temporary Fencing & Site Access Inspection