Soldier Pile Installation Checklist: verify spacing, plumb, embedment
Definition: Soldier Pile Installation Checklist guides site engineers to verify spacing, plumb, embedment depth, corrosion protection, and cap details for secure, compliant foundations, excluding lagging installation activities.
- Confirm layout spacing and offsets with survey control for accurate wall lines.
- Maintain plumbness and embedment to design for stability and serviceability.
- Verify coatings, galvanic measures, and cap details to mitigate corrosion.
- Interactive, commentable workflow with evidence capture, export, and QR code.
Soldier Pile Installation Checklist helps field teams verify spacing, plumb, embedment depth, corrosion protection, and cap details for soldier pile installation. This focused scope addresses core soldier piles QA while excluding all lagging works. Within the retaining wall foundation trade, soldier piles—often H‑pile soldier beams—must be set out precisely and kept vertical to achieve design performance. Incorrect centerline spacing, poor verticality, or inadequate embedment can lead to wall deflection, overstress, and costly rework. Equally, corrosion protection and the pile head/cap interface influence long‑term durability and tolerance control for follow‑on works. By standardizing survey practices, acceptance tolerances, and evidence capture, this checklist reduces ambiguity and speeds sign‑off per approved project specifications and authority requirements. Use it to align site engineers, surveyors, drillers, and inspectors around measurable outcomes and documented proof, ensuring every installed pile is locatable, plumb, adequately embedded, protected, and cap‑ready. Start interactive mode to tick items, add comments, and export PDF/Excel with QR verification.
- Focuses on layout spacing, offsets, and verticality tolerances to achieve accurate wall alignment and minimize rework. Captures survey evidence, centerline measurements, and tip elevations so each pile’s coordinates and orientation are traceable for as‑built records.
- Controls embedment through measured depths, geotechnical confirmations, and backfill volume checks. Ensures cut‑off elevations and flat bearing surfaces, setting reliable foundations for cap works and subsequent trades without including any lagging activities.
- Strengthens durability by verifying surface preparation, coating thickness, and holiday testing, plus cap plate fit, welding documentation, and bolt pattern tolerances. Clear acceptance criteria keep inspectors and contractors aligned with project specifications.
- Interactive online checklist with tick, comment, and export features secured by QR code.
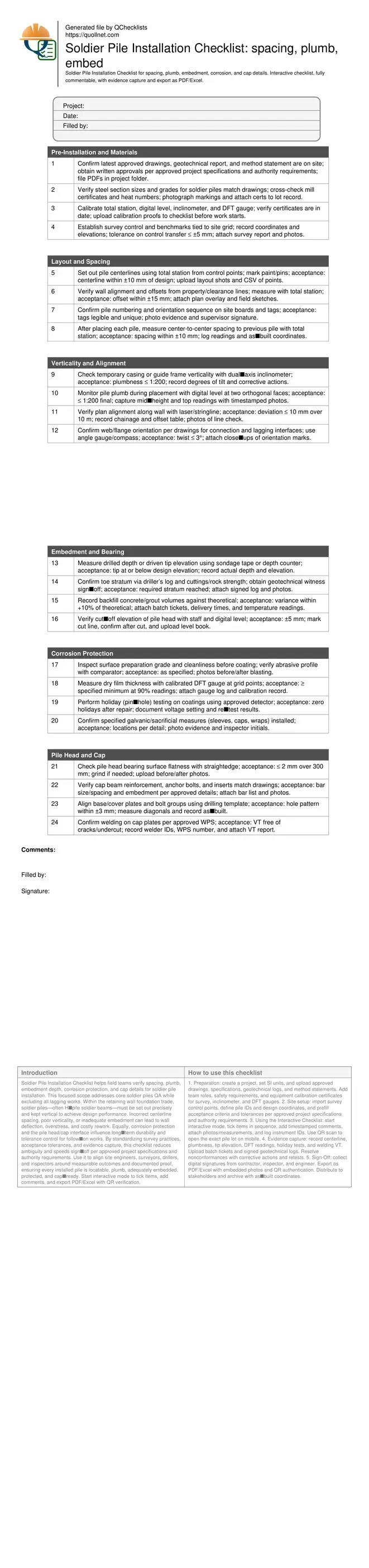
Pre-Installation and Materials
Layout and Spacing
Verticality and Alignment
Embedment and Bearing
Corrosion Protection
Pile Head and Cap
Layout and Spacing Control
Accurate layout is the backbone of soldier pile performance. Begin with stable survey control tied to the site grid, then set each centerline using a total station rather than tape offsets to reduce cumulative error. Mark centerlines and offsets visibly on the ground and on steel. Spacing tolerance should be tight enough to avoid downstream clashes with caps and tiebacks. After each pile is set, re‑measure center‑to‑center spacing and update an as‑built table with coordinates and elevations. Pay attention to property lines and underground constraints, validating clearances with plan overlays. Because soldier piles often sit adjacent to live infrastructure, build in a peer check before drilling or driving. Small layout deviations compound quickly along a wall, so detect drift early and correct at the next pile instead of forcing a mid‑wall bend. Document every survey check with photos and CSV exports to ensure traceability during design reviews and approvals.
- Use total station for centerlines, not tape alone.
- Hold spacing within ±10 mm to prevent cumulative drift.
- Update as‑built coordinates after each pile set.
- Validate offsets near property and utilities.
- Peer review layout before commencing production.
Verticality, Orientation, and Embedment
Verticality is critical to stiffness and wall deflection control. Use a dual‑axis inclinometer or digital level to monitor plumbness during placement, documenting readings at mid‑height and top. Maintain a practical tolerance of 1:200 or better. Confirm web orientation for connection details; even minor twist can complicate cap and tieback works. For embedment, measure drilled or driven depth and determine tip elevation against design, corroborated by driller’s logs and geotechnical witness. If the bore partially collapses, record depth immediately upon reaching design, then cross‑check backfill volumes against theoretical to validate embedment. Verify cut‑off elevation with a level and adjust by grinding or cutting to bring the pile head within tolerance. Solid evidence—photos, logs, and signatures—prevents disputes and accelerates approvals per approved project specifications and authority requirements.
- Record plumbness at two faces; target ≤ 1:200.
- Confirm web orientation within ≤ 3° twist.
- Measure tip elevation and log stratum reached.
- Validate backfill volume against theoretical.
- Check cut‑off elevation to ±5 mm.
Corrosion Protection and Cap Readiness
Durability starts with correct surface preparation and verified coating thickness. Confirm blast cleanliness and profile, then measure dry film thickness at a defined grid using a calibrated gauge. Scan for holidays with an approved detector and repair per specification before retesting. Where specified, install sleeves, wraps, or galvanic measures to protect the splash zone. At the pile head, achieve a flat bearing surface and confirm elevation ahead of cap works. Fit plates and bolt groups using templates to hold hole patterns within millimetre tolerances, and document all welding under an approved WPS with a visual examination record. These steps ensure the pile is not only structurally sound today but remains serviceable for the design life, enabling smooth integration with cap beams and follow‑on trades without rework.
- Verify surface prep grade and cleanliness.
- Measure DFT; meet specified minimum.
- Perform holiday testing and repair defects.
- Hold bolt patterns within ±3 mm.
- Document WPS, welder IDs, and VT results.
How to Use This Soldier Pile Installation Checklist
- Preparation: create a project, set SI units, and upload approved drawings, specifications, geotechnical logs, and method statements. Add team roles, safety requirements, and equipment calibration certificates for survey, inclinometer, and DFT gauges.
- Site setup: import survey control points, define pile IDs and design coordinates, and prefill acceptance criteria and tolerances per approved project specifications and authority requirements.
- Using the Interactive Checklist: start interactive mode, tick items in sequence, add timestamped comments, attach photos/measurements, and log instrument IDs. Use QR scan to open the exact pile lot on mobile.
- Evidence capture: record centerline, plumbness, tip elevation, DFT readings, holiday tests, and welding VT. Upload batch tickets and signed geotechnical logs. Resolve nonconformances with corrective actions and retests.
- Sign-Off: collect digital signatures from contractor, inspector, and engineer. Export as PDF/Excel with embedded photos and QR authentication. Distribute to stakeholders and archive with as‑built coordinates.
Call to Action
- Start Checklist Tick off tasks, leave comments on items or the whole form, and export your completed report to PDF or Excel—with a built-in QR code for authenticity.
- Download Excel - Soldier Pile Installation Checklist
- Download PDF - Soldier Pile Installation Checklist
- View Image - Soldier Pile Installation Checklist